Cycle Therapy (49 Offers)
Post Cycle Therapy vs. During Cycle Therapy: Understanding the Differences
When it comes to anabolic steroid use, understanding the nuances of post cycle therapy (PCT) and during cycle therapy is crucial for optimizing health and achieving desired results. Many individuals looking to enhance their physique or athletic performance often overlook the importance of these therapies, which can significantly impact recovery and hormonal balance. In this article, we'll explore the distinctions between PCT and during cycle therapy, their purposes, and key components like Clomid, HCG, and other medications.
What is Post Cycle Therapy?
Post cycle therapy is a regimen that follows a steroid cycle with the primary goal of restoring the body's natural hormone balance after synthetic hormones have been introduced. When someone uses anabolic steroids, the body's natural testosterone production can be suppressed. Consequently, PCT is essential to help stimulate this production and minimize potential side effects that may arise from hormonal imbalances, such as muscle loss, fatigue, and mood swings.
Typically, PCT involves medications that encourage the testicles to produce testosterone and mitigate estrogenic side effects. Common drugs used in PCT include Clomid (clomiphene citrate) and Nolvadex (tamoxifen). Clomid works by blocking estrogen receptors in the hypothalamus, leading to increased secretion of hormones that stimulate the testes, thus boosting testosterone levels. On the other hand, Nolvadex also acts as an estrogen blocker but is often used to prevent gynecomastia, a condition characterized by enlarged male breast tissue.
Another important medication often included during PCT is Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG). HCG mimics luteinizing hormone (LH), stimulating the testes directly to promote natural testosterone production.
What is During Cycle Therapy?
During cycle therapy focuses on managing the side effects of anabolic steroids while still using them. The main objective here is to minimize potential risks, such as hormonal imbalances and undesirable side effects, without interrupting the steroid cycle itself. During the use of steroids, many users incorporate medications to mitigate risks such as estrogen conversion, which can lead to conditions like gynecomastia and water retention.
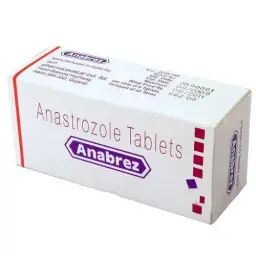
Two of the most commonly employed medications for during cycle therapy are Exemestane and Anastrozole. Both of these drugs are aromatase inhibitors (AI), meaning they prevent the conversion of testosterone into estrogen. By lowering estrogen levels, users can reduce the risk of developing gynecomastia and other estrogen-related side effects.
Exemestane is a steroidal AI that not only reduces estrogen levels but also may possess some anti-androgenic properties, making it a favorable choice for many users.
Anastrozole, a non-steroidal AI, is widely recognized for its effectiveness in minimizing estrogen levels while allowing testosterone to exert its anabolic effects.
Understanding the differences between PCT and during cycle therapy is vital for anyone looking to use anabolic steroids responsibly. While during cycle therapy focuses on immediate management of side effects, post cycle therapy aims to restore natural hormone levels after cycling.

Manufacturer: Kalpa Pharmaceuticals
Substance: Anastrozole
Pack: 30 tablets (1 mg/tab)
Key Differences Between Post Cycle Therapy and During Cycle Therapy
While both post cycle therapy and during cycle therapy are integral parts of the steroid use process, they serve distinct functions and involve different strategies:
1. Timing: As the names suggest, PCT occurs after completing a steroid cycle, while during cycle therapy is conducted simultaneously with the use of steroids.
2. Purpose: PCT's main goal is to restore the body's natural testosterone production and balance hormones, whereas during cycle therapy aims to manage side effects and maintain overall hormonal stability throughout the steroid cycle.
3. Medications Used: The medications used in each therapy differ. PCT typically involves Clomid, Nolvadex, and HCG to stimulate testosterone production and prevent estrogenic effects post-cycle. In contrast, during cycle therapy frequently includes aromatase inhibitors like Exemestane and Anastrozole to control estrogen levels during the steroid cycle.
4. Outcome Focus: PCT seeks to counteract the suppression of natural hormone production, aiming for a smooth recovery and minimal muscle loss. During cycle therapy emphasizes preventing immediate side effects linked to steroid use while maximizing the benefits of the steroids taken.
Conclusion: Making Informed Choices
Both post cycle therapy and during cycle therapy play essential roles in the world of anabolic steroids. Understanding when and how to implement these therapies can have a significant impact on your overall health and well-being. For anyone considering a steroid cycle, it's crucial to educate yourself about the potential risks and benefits associated with these therapies.
Consulting a healthcare professional who understands anabolic steroids and their effects can provide personalized guidance tailored to your specific needs. By prioritizing both during cycle therapy and post cycle therapy, you can enhance your gains while safeguarding your long-term health. As always, informed choices lead to better outcomes, so take the time to research and prepare for your journey in the world of performance enhancement.